Telephony Network Service (MANO) Example
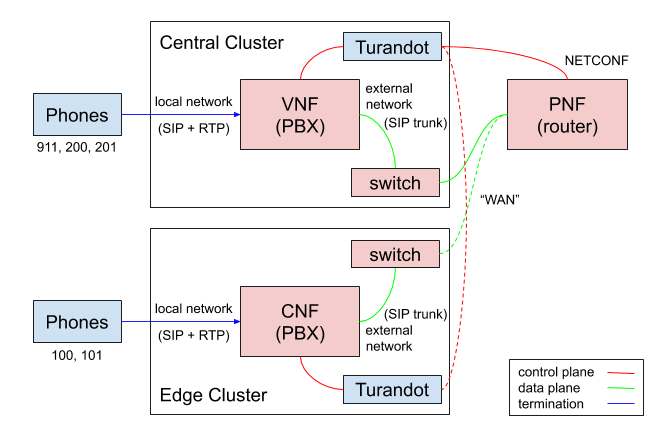
This example of a multi-cluster network service comprises a VNF (Virtualized Network Function), a CNF (Containerized, or Cloud-native Network Function), and a PNF (Physical Network Function).
It provides an end-to-end telephony service based on Asterisk PBX between a central site and an edge site. An SIP/RTP trunk is set up on a data plane, which is implemented as simple routing for demonstration purposes, but could be extended to a full-blown SD-WAN. The result is that SIP phones connected to either site can all call each other.
The entire example is also available as a set of independent Kubernetes manifests and scripts, without TOSCA and Turandot’s orchestration. See the repository.
Helper Scripts
- Build Asterisk CNF container image
- Build Asterisk VNF virtual machine image
- Save container images as tarballs
- Package all components as CSAR files
Standing Up the Router PNF
TODO
Deploying the Network Service
You will need two Kubernetes clusters to run this demo. Let’s call them “central” and “edge”.
Make sure Multus is installed on both clusters, and that KubeVirt is installed on the “central” cluster.
Note that it is possible to run multiple instances of Minikube on the same machine. E.g.:
minikube start --profile=central ...
minikube start --profile=edge ...
Let’s install Turandot on the “central” cluster. You can use the --kubeconfig switch to specify the
config for that cluster (default is at ~/.kube/config), or in the case of Minikube switch to it
using a command:
minikube profile central
turandot install --site=central --namespace=workspace --wait
Note that install will create the namespace if it does not exist. Let’s set that namespace as our
default so that we don’t have to specify it from now on:
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=workspace
We’ll set up a delegate to the “edge” cluster. If you have a separate config file for it, use the
--delegate-kubeconfig switch. Or if it’s stored in a separate context within the default config (which
is the case with Minikube), use --delegate-context:
turandot delegate set edge --delegate-context=edge
Let’s register all our CSARs in the repository:
turandot template register telephony-network-service --file=dist/telephony-network-service.csar
turandot template register simple-data-plane --file=dist/simple-data-plane.csar
turandot template register asterisk-cnf --file=dist/asterisk-cnf.csar
turandot template register asterisk-vnf --file=dist/asterisk-vnf.csar
Finally, let’s deploy:
turandot service deploy telephony-network-service --template=telephony-network-service
You should see Asterisk VNF and the data plane deployed on the “central” cluster, and then Turandot installing itself on the “edge” cluster, where it will deploy Asterisk CNF and the data plane. Finally the VNF and CNF will self-configure, Turandot will configure the PNF, and the network service will be up.